Hepatitis B Virus
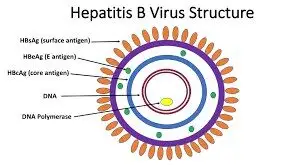
What is HBsAg?
HBsAg, which stands for Hepatitis B surface antigen, is a protein that exists on the surface of the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). When a blood test detects HBsAg, it indicates that a person is currently infected with the Hepatitis B virus. This test is the most common way to diagnose an active hepatitis B infection.
What Does a Positive HBsAg Test Mean?
A “positive” or “reactive” HBsAg test result signifies that you have an active hepatitis B infection and are contagious. This means the virus is present in your blood and other bodily fluids, and you can transmit it to others.
- Acute Infection: If the HBsAg test is positive for less than six months, it’s considered an acute infection. Most adults will clear the virus on their own and develop immunity.
- Chronic Infection: If the test remains positive for more than six months, it’s considered a chronic infection. People with chronic hepatitis B may not have symptoms but can still transmit the virus. They are also at a higher risk of developing serious liver conditions like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
How is Hepatitis B Transmitted?
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious virus that is spread through contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. It is not spread through casual contact like hugging, kissing, or sharing food and water.
Common transmission routes include:
- Sexual contact: Unprotected sex with an infected person is a major mode of transmission.
- Sharing needles: Reusing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
- Mother to child: An infected mother can pass the virus to her baby during childbirth.
- Sharing personal items: This includes items like razors, toothbrushes, or nail clippers that may have trace amounts of blood on them.
- Healthcare settings: Accidental needle sticks or exposure to infected blood in a professional setting.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B
Many people with hepatitis B, particularly those with a new infection, may have no symptoms at all. When symptoms do appear, they can range from mild to severe and may include:
- Flu-like symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and body aches.
- Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Dark-colored urine and pale stools.
Diagnosing
Diagnosing a Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection primarily relies on a series of blood tests that detect specific antigens and antibodies. The presence of Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is the key indicator of an active infection.
Here’s how the diagnosis works:
- HBsAg Test: The HBsAg test is the primary screening tool. It detects a protein on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. A positive or “reactive” HBsAg result means the person is currently infected with HBV and is contagious. The antigen becomes detectable in the blood approximately 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. If the HBsAg remains positive for more than six months, the infection is classified as chronic.
- Hepatitis B Panel: To get a full picture of the patient’s status, doctors typically order a “Hepatitis B Panel,” which includes other important tests:
- Hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs): The presence of this antibody indicates a person is immune to HBV. This immunity can be due to a successful vaccination or a resolved, past infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc): This antibody indicates a person has been exposed to the virus at some point in their life, either recently or in the past. It does not provide immunity.
By interpreting the combination of these three test results, a healthcare provider can determine if a person has an acute or chronic infection, is immune from a past infection or vaccination, or is susceptible to the virus and needs to be vaccinated. Additional tests, such as a liver function test or an HBV DNA test, may be used to assess the level of liver damage and viral replication.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and is not a replacement for professional medical guidance. Please consult with a medical professional, such as those at Rajavarma Siddha Hospital, for personalized advice


